No-Third-Party Trust Framework
In decentralized network like Otmoic, ensuring trust, security, and compliance without relying on centralized intermediaries is crucial. Otmoic achieves this through an integrated framework built on:
- Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
- An autonomous reputation system based on Olares ID
- Comprehensive KYC processes for both users and liquidity providers (LPs).
Verifiable Credential (VC)
A VC is essentially a cryptographically signed statement issued by an Issuer about a Holder (or subject). This credential allows you to provide specific attributes of your identity or qualifications without relying on centralized authorities or revealing your entire identity. VCs operate within a three-party model: the Issuer, Holder, and Verifier.
The inherent privacy-preserving qualities make them a cornerstone of trust within the Otmotic ecosystem:
- The cryptographic nature of VCs ensures their authenticity and makes them resistant to tampering or forgery.
- VCs are represented as JSON objects, facilitating straightforward programmatic handling across diverse platforms.
- By using VCs, participants can validate their qualifications and authorizations quickly and securely while maintaining privacy in online transactions.
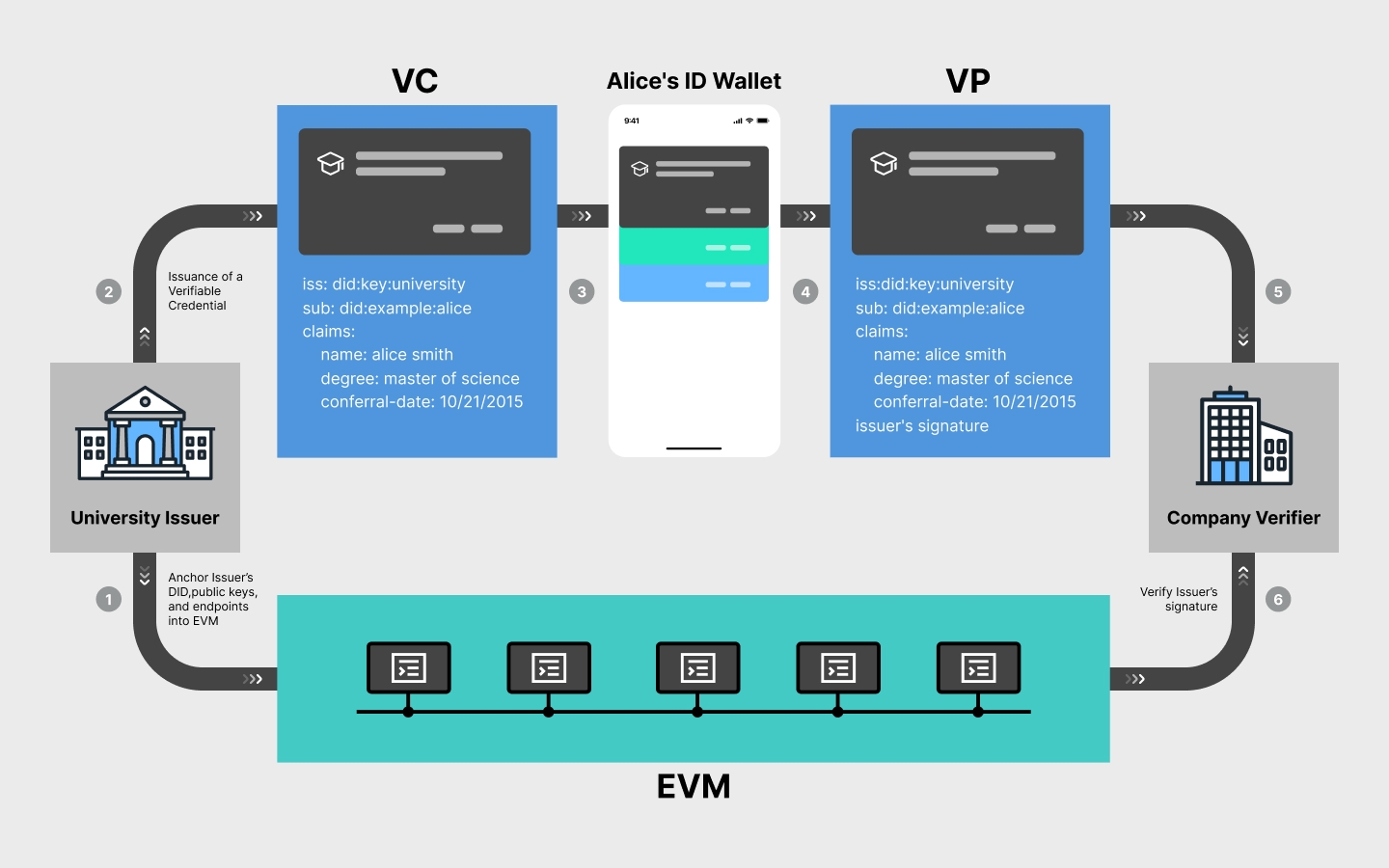
Learn more about VC and its process in Snowinning Protocol.
Reputation System
The Reputation System for Otmoic provides a decentralized method of evaluating the credibility and reliability of transaction participants. Built on the Snowinning Protocol, it integrates DIDs and VCs to ensure transparency, control, and trust among users.
Advantages of Otmoic's reputation system
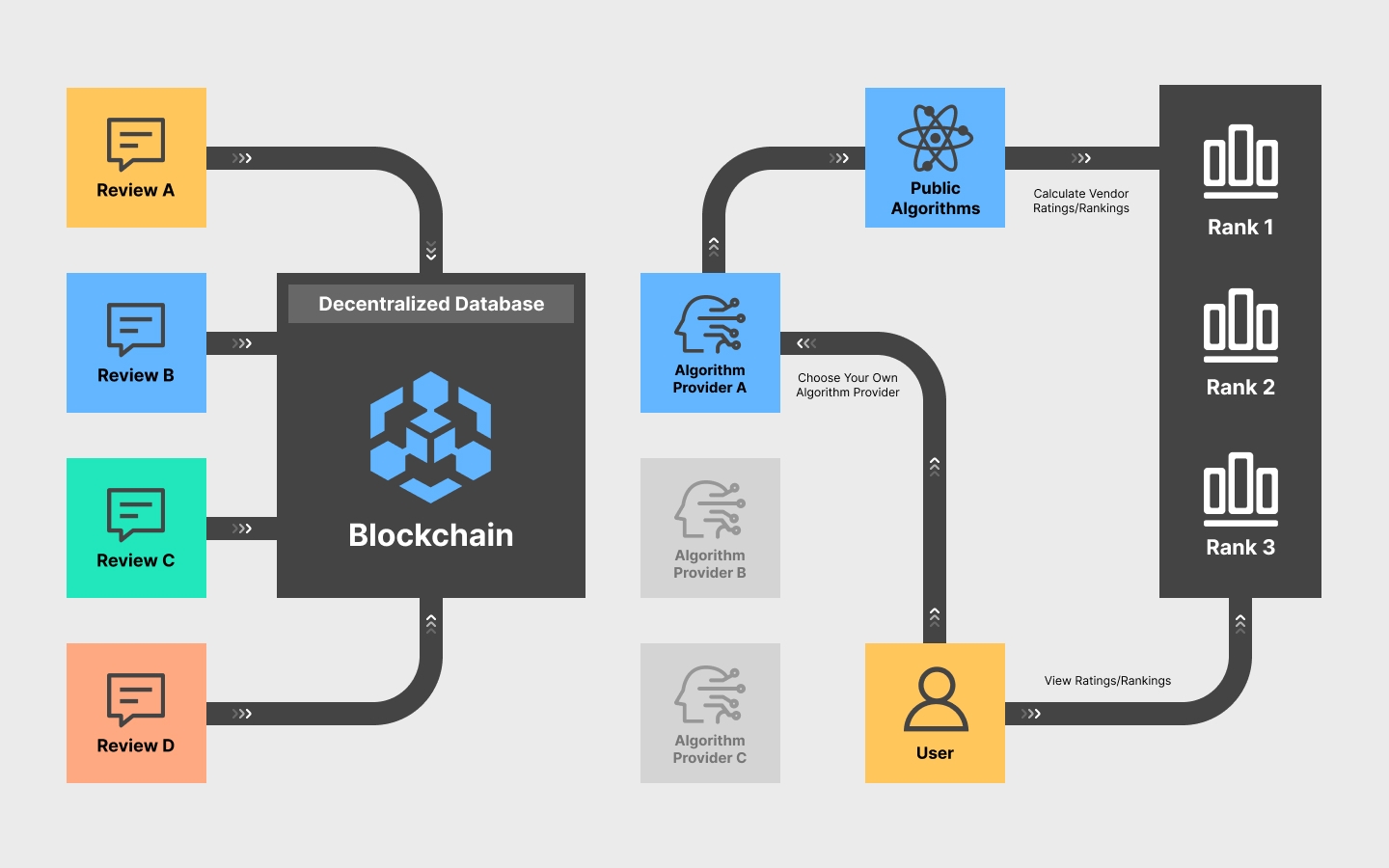
- Decentralized raw data collection: Reputation data is recorded directly on the blockchain via smart contracts, ensuring authenticity and immutability. This approach provides an indisputable record of user interactions and ratings.
- Open algorithms: Unlike opaque traditional systems, the Snowinning Protocol promotes transparency by allowing reputation algorithms to be openly published. Users can choose which algorithms to trust for generating reputation scores, fostering trust and adaptability.
- Customized reputation processing: Users can access raw reputation data and process it according to their specific requirements, enabling tailored insights and a more equitable assessment of participants.
- Reputation distribution: The system distributes reputation data through the Otmoic protocol, allowing participants to access reliable, decentralized reputation scores from multiple sources, promoting informed decisions.
How reputation is created for Otmoic
In the Snowinning Protocol, abstract entities such as movies, agents, and market makers can be represented through DIDs using entity domains. This allows for the creation of tailored reputation systems for these non-traditional entities.
The Otmoic Reputation Contract leverages EIP-712 signatures for authenticating DID ownership and logs complaints related to bids in an entity with tag otmoic.reputation tag. This approach strengthens the reliability of interactions and improves the resolution process by ensuring that all reputation data is transparent and verifiable.
KYC in Otmoic
The Otmoic Protocol incorporates a streamlined KYC process to ensure regulatory compliance while preserving user privacy and security.
KYC for Users
KYC for users involves the following steps:
- Obtain a DID: Users generate and manage their DIDs through an identity wallet app.
- Submit KYC documents: Users complete a KYC form and upload required identification documents through the web interface. The submission is digitally signed using LarePass, the wallet app.
- Validation by the relay server: The submitted information is forwarded to the relay server for thorough validation.
- Receive VC certificate: Once validated and approved, users receive a VC certifying their KYC status, securely stored in LarePass
- Eligibility for transactions: With the VC, users can seamlessly participate in transactions across the network, proving KYC compliance when necessary.
This DID-based KYC system enhances security, privacy, and ease of use, promoting user trust and regulatory adherence within decentralized ecosystems.
KYC for LPs
Otmoic’s Blockchain Edge Client architecture supports the formation of specialized LP node sub-networks through relay servers, enabling enhanced regulatory compliance. This architecture allows participants to voluntarily form sub-networks under specific rules, such as:
- Regulatory-Specific Relays: For instance, a relay server compliant with US KYC and AML regulations can be established. Such a relay will only process requests to and from LP nodes and user wallet addresses that meet US compliance standards.
- Maintained Whitelists: Relay servers maintain lists of compliant LP nodes and user addresses. Dapp web UIs provide straightforward tools for LPs and users to register using their verified credentials.
- Enhanced Compliance and Flexibility: Despite adding compliance mechanisms, this approach paradoxically strengthens censorship resistance by allowing participants to choose sub-networks freely and without extra obligations.