How Otmoic Works
At the core of Omotic’s design is a groundbreaking shift from conventional shared liquidity pools to a network of Liquidity Provider (LP) nodes. This architecture harnesses automated software agents to facilitate decentralized, real-time asset exchanges and ensure seamless liquidity within the network.
Edge-client architecture
Omotic’s LP nodes operate as blockchain edge nodes running on Olares, a decentralized sovereign cloud platform. Those edge nodes communicate with the Obridge, the Otmoic client, to provide a DApp UI to users.
- The LP pre-determines the types of exchanges it wants to participate in, fund the wallets, and store the private keys on the edge node.
- The "always-on" software agents can be matched to exchange with users at all times, and hence provide instant liquidity. They are capable of performing complex interactions in atomic swaps on behalf of the LPs.
- The edge nodes offer "exchange rates" on behalf of LPs when bridging cross-chain token exchanges. Multiple LP edge nodes compete to offer the best exchange rates for each user request.
- Each node is equipped with Olares ID and Verifiable Credentials (VCs) for robust identity verification and on-chain reputation tracking. This ensures that every node’s actions are secure and traceable, fostering trust in the network.
Relay
The Otmoic relay server serves as a crucial component within the Otmoic ecosystem, acting as the backend infrastructure for the Otmoic client app. Its primary function is to coordinate communication between users and LP nodes to facilitate seamless transactions.
- Registry maintenance: The relay server keeps an updated record of all active LP edge nodes within the network. This registry includes vital details about each LP’s exchange capabilities, allowing for efficient matching during transaction requests.
- Transaction coordination: When a user initiates a bridge exchange through the client app, the relay server acts as the intermediary that matches the user’s request to the most suitable LP edge node based on the defined exchange criteria.
- Decentralized price discovery: Relay enables a decentralized pricing mechanism by allowing multiple LP nodes to submit their exchange rates in response to a user’s request. This fosters a competitive, market-driven environment and negates the need for centralized oracles to provide price feeds.
In a truly decentralized and permissionless fashion, anyone can create a UI frontend and start a relay server for Otmoic and users can choose a relay system without constraints.
Otmoic workflow
Otmoic is initially designed for cross-chain token exchange, but this model underpins the e-commerce ecosystem and has been proven scalable in real-world application scenarios. The following chart illustrates the Otmoic workflow with a video service transaction case:
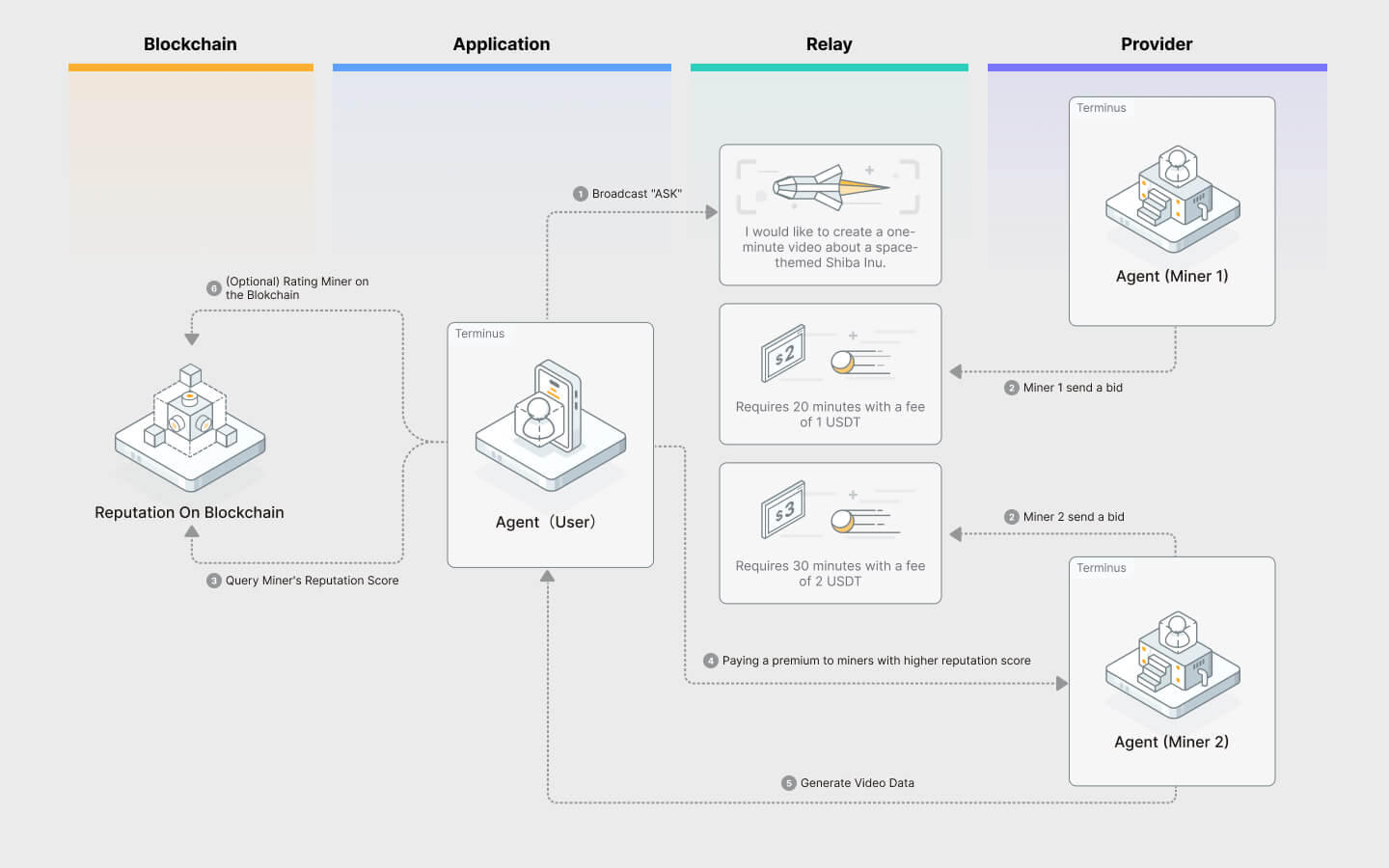
- The application initiates a transaction by sending an ASK (a RFQ) to the relay. This ASK outlines the desired service or asset parameters, initiating the RFQ-based price discovery process. Before initiating a transaction, the user (application) must have completed a KYC process based on Olares ID.
- Relay broadcasts the ASK to a network of liquid or service providers. These providers are equipped with Olares IDs and Verifiable Credentials (VCs) for secure identification and reputation tracking.
- Providers send their Bids back to Relay. During this process, the LP nodes rely on Automatic Market Making (AMM) to automatically balance its liquidity provisioning and calculate the bids.
- Relay aggregates and returns bids to the application.
- Application selects a provider based on the bid and the provider's reputation, and completes the payment. Providers with higher scores to stand out as more reliable choices.
- Provider delivers services to the application. This fulfills the the price discovery process and the atomic swap process.
- Application reviews the provider's service. This review updates the on-chain Reputation of the Provider, impacting future interactions and supporting a transparent, reliable ecosystem.