Atomic Swap in Otmoic
With the RFQ protocol and price discovery mechanism in place, Otmoic support the following "swaps":
- Single-chain trade
- Cross-chain bridge
- Over-the-counter (OTC) transactions
Prerequisites
- Users, relay servers, and LPs possess Olares IDs (DIDs) and operate on active Olares nodes linked to their DIDs.
- Users have completed KYC with the relay server and obtained a Verifiable Credential (VC).
Single-chain trade
An Hashed Timelock Contract (HTLC) is a type of smart contract used to facilitate trustless transactions between parties by ensuring that funds are only transferred if a cryptographic condition is met within a specified time. If the condition isn’t met, the contract refunds the funds to the original sender after the time expires. Here is how you can HTLC-based trade on Ethereum using the RFQ protocol and price discovery mechanism of Otmoic. We will use Alice as the user who wants to exchange ETH for USDT over the Otmoic network:
Alice submits an ASK (Request for Quote, or RFQ) to the relay server.
The server broadcasts the RFQ to eligible liquidity provider (LP) nodes that support the requested trading pair (ETH/USDT).
LP nodes assess their liquidity and respond with BIDs, each representing an offer with a specific exchange rate and associated terms.
The relay server aggregated and returned the BIDs to Alice.
Alice receives the aggregated BIDs from the relay, and selects the most favorable one based on factors like price and reputation.
Alice sets up a HTLC contract to facilitate the swap. This contract acts as an automated escrow, holding both ETH and USDT until conditions for the trade are met.
Alice (the sender) uses her private key to create an HTLC on Ethereum, locking the ETH with a hashed secret.
LP sees the HTLC and deposit the agreed upon amount of USDT into the HTLC.
The conditions are met when HTLC receives the USDT from the LP. The smart contract automatically transfer the USDT to Alice,and release the ETH to the LP.
NOTE
If conditions are not met within a specified timeframe as specified in HTLC, for example, if the LP doesn't deposit in time or put in enough tokens, Alice can simply wait for the HLTC to expire.
Alice reviews the provider's service.
Cross-chain bridges
The current gold standard for cross-chain transactions is Atomic Swap. That is to rely on off-chain actors to validate transactions in a trustless manner and record the results in on-chain smart contracts.
To illustrate how atomic swaps work as cross-chain bridges, or bridges, let’s say that Alice holds a token on chain A, and Bob holds a token on chain B. They want to do a swap, allowing Alice to move her token from chain A to chain B, and vice versa for Bob. An atomic swap consists of multiple steps performed by both Alice and Bob, and the swap is only successful after all the steps are successful. If any one of them fails to perform any step, the swap will not happen, and they will each still hold their original tokens.
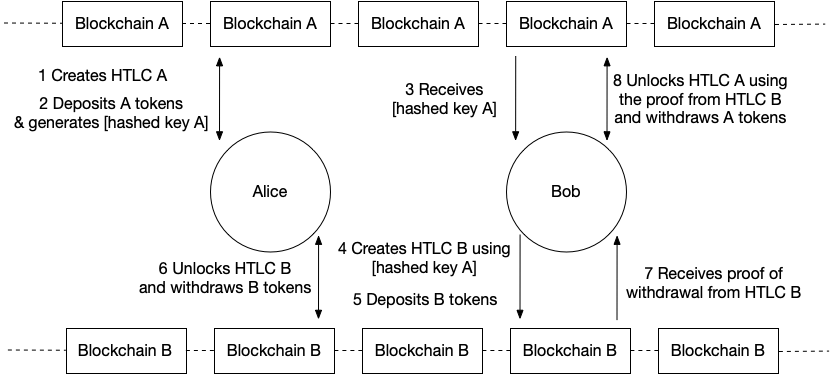
Alice uses her private key A to create a Hashed Timelock Contract (HTLC) on chain A.
Alice deposits her tokens to HTLC A. The contract generates a hashed key A and stores it in HTLC A for the public to see.
Bob sees hashed key A and wants to trade with Alice.
Bob uses his private key B and hashed key A to create another HTLC on chain B.
Bob deposits his tokens to the HTLC B he just created on chain B.
If Alice is satisfied that Bob puts enough tokens in HTLC B, Alice uses her private key A to unlock HTLC B and withdraws Bob’s tokens.
In the process, HTLC B will record proof of withdrawal in HTLC B for everyone to see.
Bob uses his private key B and the proof of withdrawal on B to unlock HTLC A and get Alice’s tokens.
All these happen without Alice or Bob knowing each other. They can use public communication channels to exchange information about the next step in the process. It is also important to note that if any party is unhappy at any time, he or she can simply refuse to perform the next step. The “timelock” in HTLC will expire after some time (eg, 2 hours), allowing each party to withdraw their original deposits. For example, if Bob does not put enough tokens into HTLC B, Alice could simply not unlock HTLC B and wait for HTLC A to expire.
The advantage of the atomic swap approach is that it is entirely decentralized and trustless. It is the “right way” to do cross-chain bridges, and is the gold standard every alternative solution must compare to.
OTC transactions
Otmoic supports seamless on-ramp (fiat → digital currency) and off-ramp (digital currency → fiat) OTC crypto transactions, providing secure and efficient transfer of funds.
The following example illustrates how Alices conducts an on-ramp transaction (USD to ETH) on the Otmoic network:
- Resolve Olares IDs: Alice’s relay server resolves and caches the current Olares IDs (DIDs) of discovered LPs to maintain reliable network status.
- Query the Relay: Alice queries the relay for the USD/ETH trading pair. The relay filters results based on active LP nodes.
- Send ASK Request: Alice selects the trading pair, specifies the desired exchange amount, and sends an ASK (Request for Quote) message to the relay server.
- Forward the ASK: The relay server forwards the ASK to LP nodes that meet the criteria.
- Evaluate and Submit BIDs: LP nodes assess the request against their liquidity and trading parameters and respond with BIDs.
- Aggregate BIDs: The relay collects BIDs from all participating LP nodes and sends them to Alice.
- Select a BID: Alice reviews the BIDs and chooses one based on the offer and the LP’s reputation.
- Deploy Smart Contract: The selected LP publishes a smart contract on the blockchain, funds it with the agreed ETH amount, and provides the contract address to Alice.
- Verify and Fund: Alice queries the contract to verify the ETH availability and then funds her wallet using her chosen fiat payment method.
- Execute Settlement: Once the LP confirms receipt of the fiat payment, they execute the smart contract, releasing the ETH to Alice’s wallet and completing the transaction.
The off-ramp process (digital currency → fiat) follows similar steps.